Admission Controller
End of Life Notice: The Sysdig Legacy Scanning Engine will reach its End of Life (EOL) on December 31st, 2024. After this date, it will no longer be supported or maintained. Please upgrade to our New Scanning Engine before December 31st, 2024 to ensure continuous service and support. For assistance, contact our support team or your account representative.
Features
Installing admission controller will enable the following:
Image Scanning Capabilities: Sysdig’s Admission Controller (UI-based) builds upon Kubernetes and enhances the capacity of the image scanner to check images for Common Vulnerabilities and Exposures (CVEs), misconfigurations, outdated images, etc., elevating the scan policies from detection to actual prevention. Container images that do not fulfill the configured admission policies will be rejected from the cluster before being assigned to a node and allowed to run.
Kubernetes Audit Logging Capabilities: Enable the
features.k8sAuditDetections=trueoption to use Kubernetes audit logging features with the admission controller. (See also: Kubernetes Audit Logging.)
Installation
Follow the standard helm installation. Replace helm install with helm upgrade --install.
To enable the admission controller (scanning legacy engine) in your existing Sysdig Secure Helm install command, add the following flags:
--set admissionController.enabled=true \
--set admissionController.sysdig.secureAPIToken=<my key> \
--set admissionController.scanner.enabled=true \
For additional configuration options, including on-premises, using a proxy, etc., see the admission-controller readme.
Usage
- Create Admission Controller policies as you see fit for your use cases
- Assign the policies to the connected clusters
- Enable the Admission Controller for the cluster
Create Admission Controller Policies
Admission Controller Policies define the criteria to accept or reject a given container image at admission time. Remember that Policies must be assigned to a cluster to be enforced.
Log in as Administrator to Sysdig Secure and select
Image Scanning> Admission Controller|Policies.The Admission Controller Policies page displays a list of any previously defined policies.
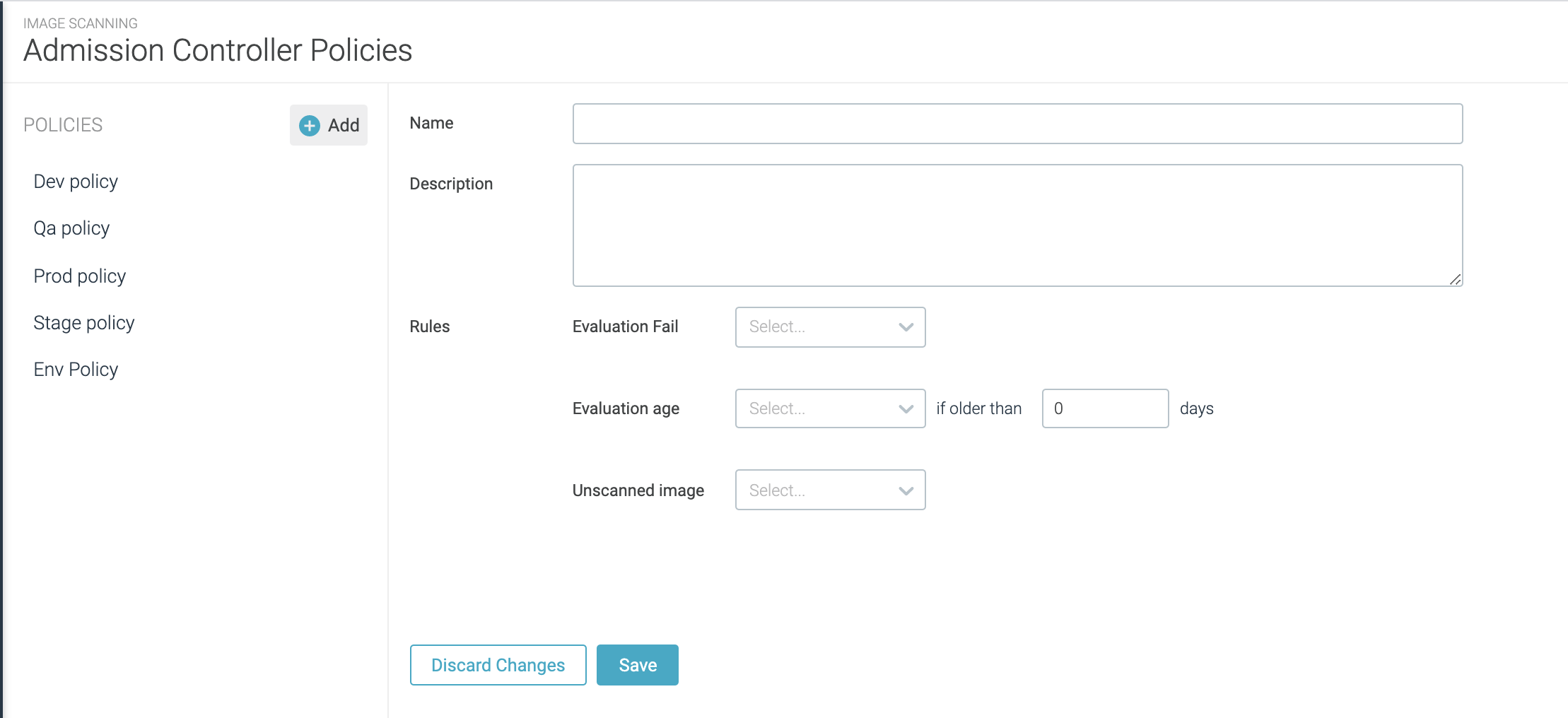
Click
+Policyand enter a meaningfulNameandDescription.Define the policy
Rules:Evaluation Failure:Whether to reject images that are failing scanning policy evaluation. Images matching a policy assignment without scan results will also be rejected.Evaluation Age:Whether to reject images when the evaluation is older than X days. You might set this condition to force a new vulnerability check, for example.Unscanned Image:Whether to reject images that do not have an existing evaluation at admission time. Choose from three options:Ignore:Ignore this conditionReject:Reject the requestReject and Scan:Reject the request and scan the image in parallel.
Typically, Kubernetes will retry creating the pending image, so eventually, the image will have a valid evaluation and then the other conditions will apply. Since scanning during admission can potentially slow down the deployment process, we don’t recommend this option unless you are confident that most images will have an evaluation before admission (i.e. instrumenting the CI/CD pipelines).
- Click
Save.
Understanding: How Policy Conditions are Applied
Policy conditions are applied using an AND operator.
For example, if I set Evaluation Fail to Reject AND Evaluation Age to Reject for older than 15 days,
then if I receive an image with an existing evaluation that is passing and that
evaluation is 20 days old, the request will be rejected.
Assign Admission Controller Policies
Log in as Administrator to Sysdig Secure and select
Image Scanning> Admission Controller|Policy Assignment.The admission controller policy assignment page displays the list of Kubernetes clusters with Admission Controllers, and their current status.
Connected/disconnected clusters: Clusters where the admission controller was never installed and will not appear at all. Otherwise:
Connected:Clusters with a connected and healthy admission controller will show under the “Connected” label.Disconnected:A Kubernetes cluster that had an admission controller installed, but the admission controller component is not reporting back to the Sysdig backend, will appear under the “Disconnected” label.
Enabled/disabled Admission Controllers: You enable/ disable the admission controller for each cluster using the switch on the top right.
Enabled:A green dot by the cluster name shows the admission controller is enabled (enforcing)Disabled:A grey dot means the admission controller is disabled.
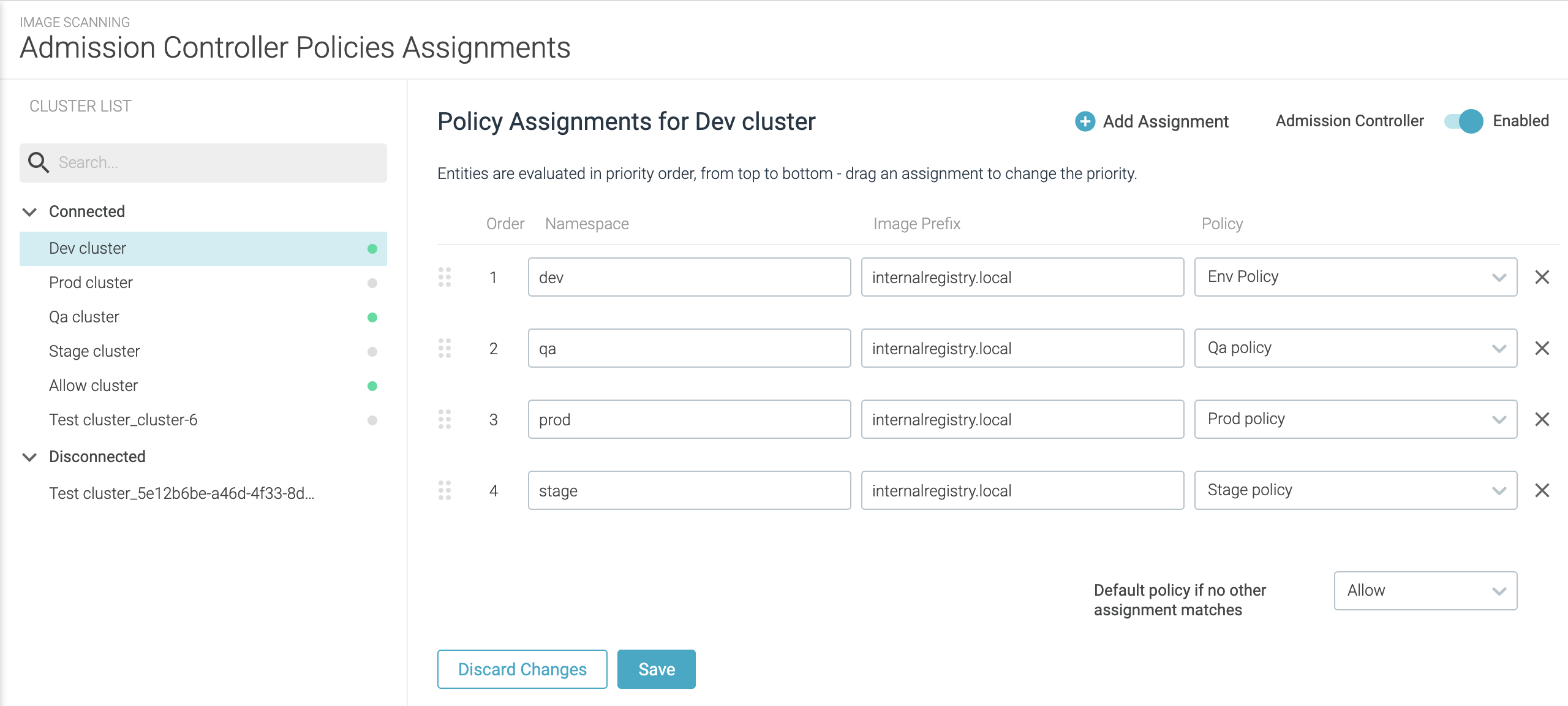
Click
+Add Assignmentand enter the basic assignment details.A cluster can have multiple assignments at different levels of granularity and the policies are evaluated from top to bottom.
Namespace: Leave blank to match any namespace, or add a regular expression to match the namespace
ex.: | field | value matches | | — | — | |dev| any namespace containing ‘dev’| |^dev| any namespace starting with ‘dev’ | |^dev$| a namespace with the exact name ‘dev’ |Prefix:Leave blank to match any image name, or limit by entering a particular prefix. For example, theredisprefix would match images declared asredis:latestorredis:v2in the container creation request.Policy:Select a policy from the drop-down list.
Choose
Default policy if no other assignment matches: Select toAllowby default orRejectby default.
Be very careful with the Reject by default option. Be sure to
explicitly allow critical workloads in your system.
- Click
Save.
Saved changes are pulled from the Admission Controller every 5 minutes
- Optional: Drag the new assignment to a different position in the evaluation list if it should be applied before another assignment.
Understanding: Evaluation Order
Assignments are evaluated from top to bottom. The first match dictates which policy will be applied.
The default cluster action will be applied if no assignment matches.
For example:
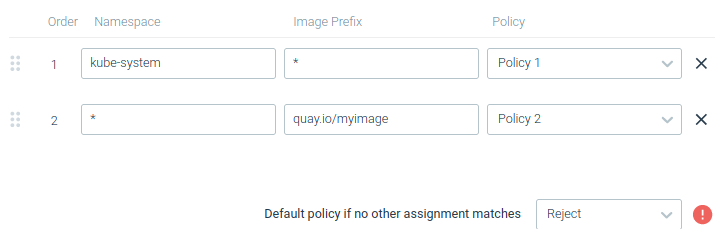
Given the following assignments:
The policies that apply would be the following
kube-systemnamespace, container with image pathdocker.io/myimage-> will applyPolicy1mynamespacenamespace, container with image pathquay.io/myimage-> will applyPolicy2mynamespacenamespace, container with image pathdocker.io/myimage-> will apply default policyRejected
Enable and Disable Admission Controller
It is recommended to develop the policies and assignments while the Admission Controller is Disabled. Enable it on a staging cluster to test
before enabling it in production.
When you are happy with the defined behavior:
Log in as Administrator to Sysdig Secure and select
Image Scanning> Admission Controller|Policy Assignment.Select the relevant cluster from the left side menu.
Slide the Admission Controller to
Enabled.Monitor any resulting events as usual.
The Disable function can also be used to quickly stop the Admission
Controller if unexpected behavior is detected that adversely affects the function of a cluster.
Verify Image Scanning Is Working
Install the Admission Controller on your Kubernetes cluster.
This feature is enabled by default through the
scanner.enabledvalue.Enable Admission Controller using Sysdig Secure > Image Scanning > Admission Controller > Policy Assignments.
This section can only be accessed by a user with Administrator permissions.
Add an assignment to Allow or Deny images within a namespace.
Tail to the logs from the Admission Controller:
kubectl logs -f -n sysdig-admission-controller -l app.kubernetes.io/component=webhookPush some deployment into your Kubernetes Cluster to watch the result, for example an nginx image
kubectl run nginx --image=nginx
If policy is set to allow, the deployment will be successful.
Either way, you should see some logs in Admission Controller tail:
```console
-- allow assignment result
{"level":"info","component":"scanning-evaluator","message":"checking pod=nginx in namespace=default"}
{"level":"info","component":"scanning-evaluator","message":"evaluating container with name=nginx and image=nginx"}
{"level":"info","component":"scanning-evaluator","time":"","message":"matched policy=Allow always for namespace=default and image=nginx"}
{"level":"info","component":"scanning-evaluator","message":"allowing container with name=nginx and image=nginx"}
-- reject assignment result
{"level":"info","component":"scanning-evaluator","message":"checking pod=nginx in namespace=default"}
{"level":"info","component":"scanning-evaluator","message":"evaluating container with name=nginx and image=nginx"}
{"level":"info","component":"scanning-evaluator","message":"matched policy=Reject Allways for namespace=default and image=nginx"}
{"level":"info","component":"scanning-evaluator","message":"denying container with name=nginx and image=nginx reason=\\"Reject Always\\""}
```
Troubleshooting
Policy Rules Are Not Honored
See Admission Controller - Understanding How Policy Conditions Are applied.
Policy Assignments order Are Not honored
It may be that you’re using the same namespace and image prefix on more than one assignment.
Changes on Policy Assignments Are Not Applied to the Cluster
Admission Controller pulls changes from the Sysdig Secure platform every 5 minutes. You can wait five minutes, or force the admission controller webhook to restart:
kubectl rollout restart deployment -n sysdig-admission-controller sysdig-admission-controller-webhook
ka.sourceips Not Supported
Admission Controller will not be able to retrieve the source IP of the events when this information is not provided by the Kubernetes Admission Controller. If you really require this field, as a workaround, you can use the legacy Sysdig Agent + Kubernetes Audit.