RedisDB
This page describes the default configuration settings, how to edit the configuration to collect additional information, the metrics available for integration, and a sample result in the Sysdig Monitor UI.
Application Setup
Redis will automatically expose all metrics. You do not need to configure anything in the Redis instance.
Sysdig Agent Configuration
Review how to Edit dragent.yaml to Integrate or Modify Application Checks.
Default Configuration
By default, Sysdig’s dragent.default.yaml uses the following code to
connect with Redis and collect basic metrics:
app_checks:
- name: redis
check_module: redisdb
pattern:
comm: redis-server
conf:
host: 127.0.0.1
port: "{port}"
Some additional metrics can be collected by editing the configuration file as shown in following examples. The options shown in Example 2 are relevant if Redis requires authentication or if a Unix socket is used.
Remember! Never edit dragent.default.yaml directly; always edit
only dragent.yaml.
Example 1: Key Lengths
The following example entry results in the metric redis.key.length in
the Sysdig Monitor UI, displaying the length of specific keys (segmented
by: key). To enable, provide the key names in dragent.yaml as
follows.
Note that length is 0 (zero) for keys that have a type other than
list, set, hash, or sorted set. Keys can be expressed as patterns;
see https://redis.io/commands/keys.
Sample entry in dragent.yaml:
app_checks:
- name: redis
check_module: redisdb
pattern:
comm: redis-server
conf:
host: 127.0.0.1
port: "{port}"
keys:
- "list_1"
- "list_9*"
Example 2: Additional Configuration Options
unix_socket_path(Optional) - Can be used if your Redis uses a socket instead of host and port.password(Optional) - Can be used if your Redis requires a password
app_checks:
- name: redis
check_module: redisdb
pattern:
comm: redis-server
conf:
host: 127.0.0.1
port: "{port}"
# unix_socket_path: /var/run/redis/redis.sock # can be used in lieu of host/port
# password: mypassword # if your Redis requires auth
Example 3: COMMANDSTATS Metrics
You can also collect the INFO COMMANDSTATS result as metrics
(redis.command.*). This works with Redis >= 2.6
Sample implementation:
app_checks:
- name: redis
check_module: redisdb
pattern:
comm: redis-server
conf:
host: 127.0.0.1
port: "{port}"
command_stats: true
Metrics Available
See RedisDB Metrics.
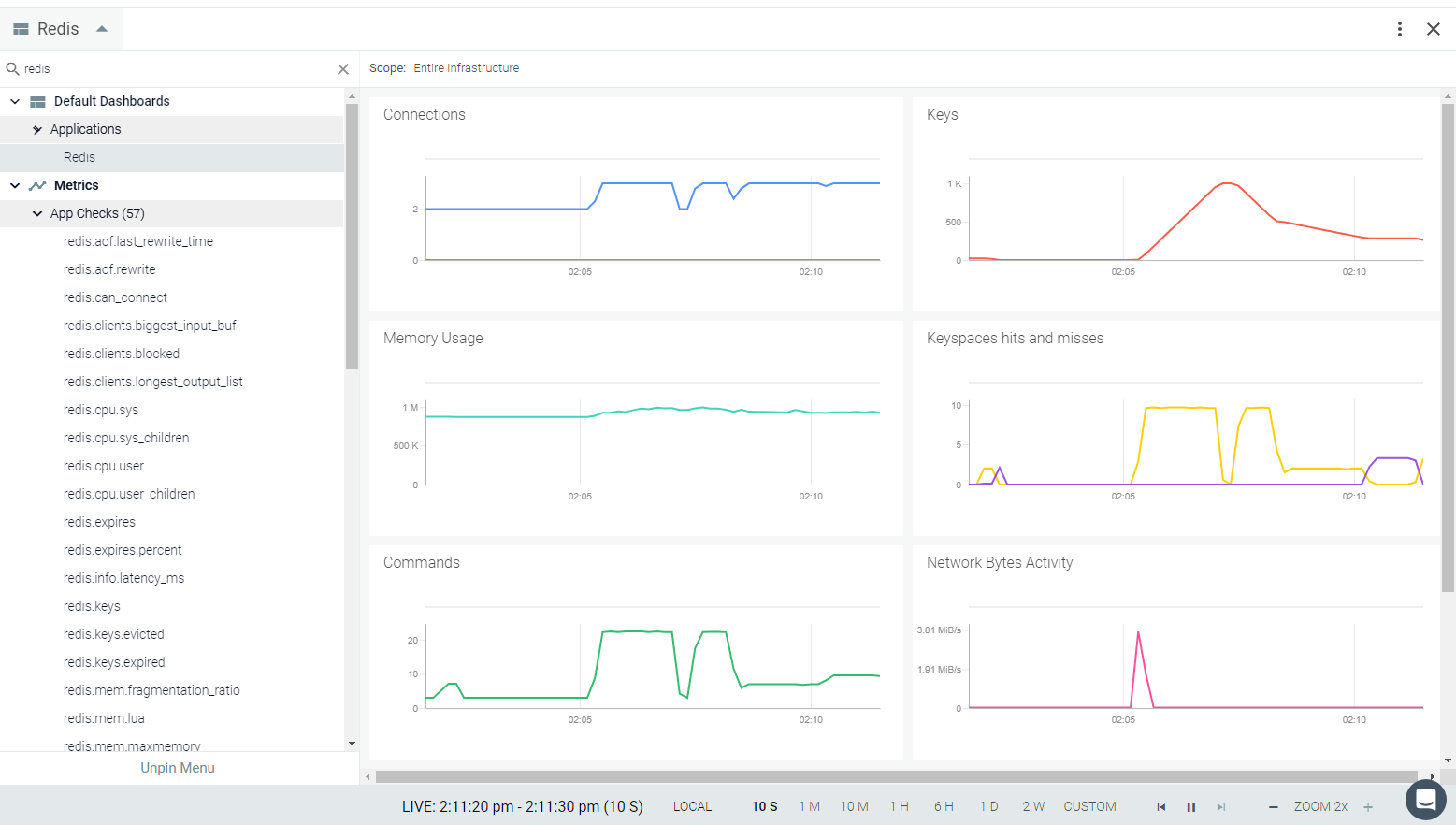
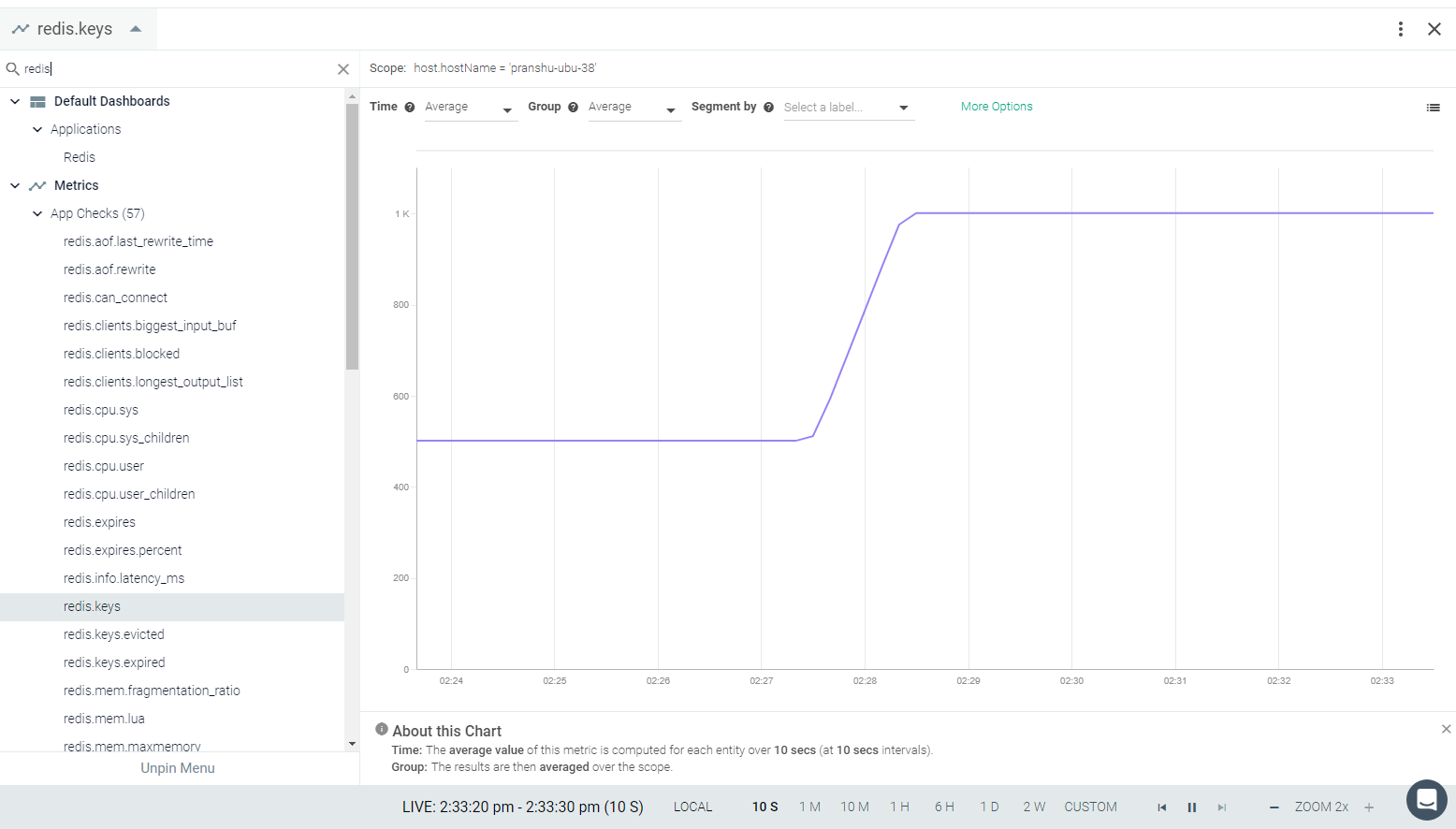
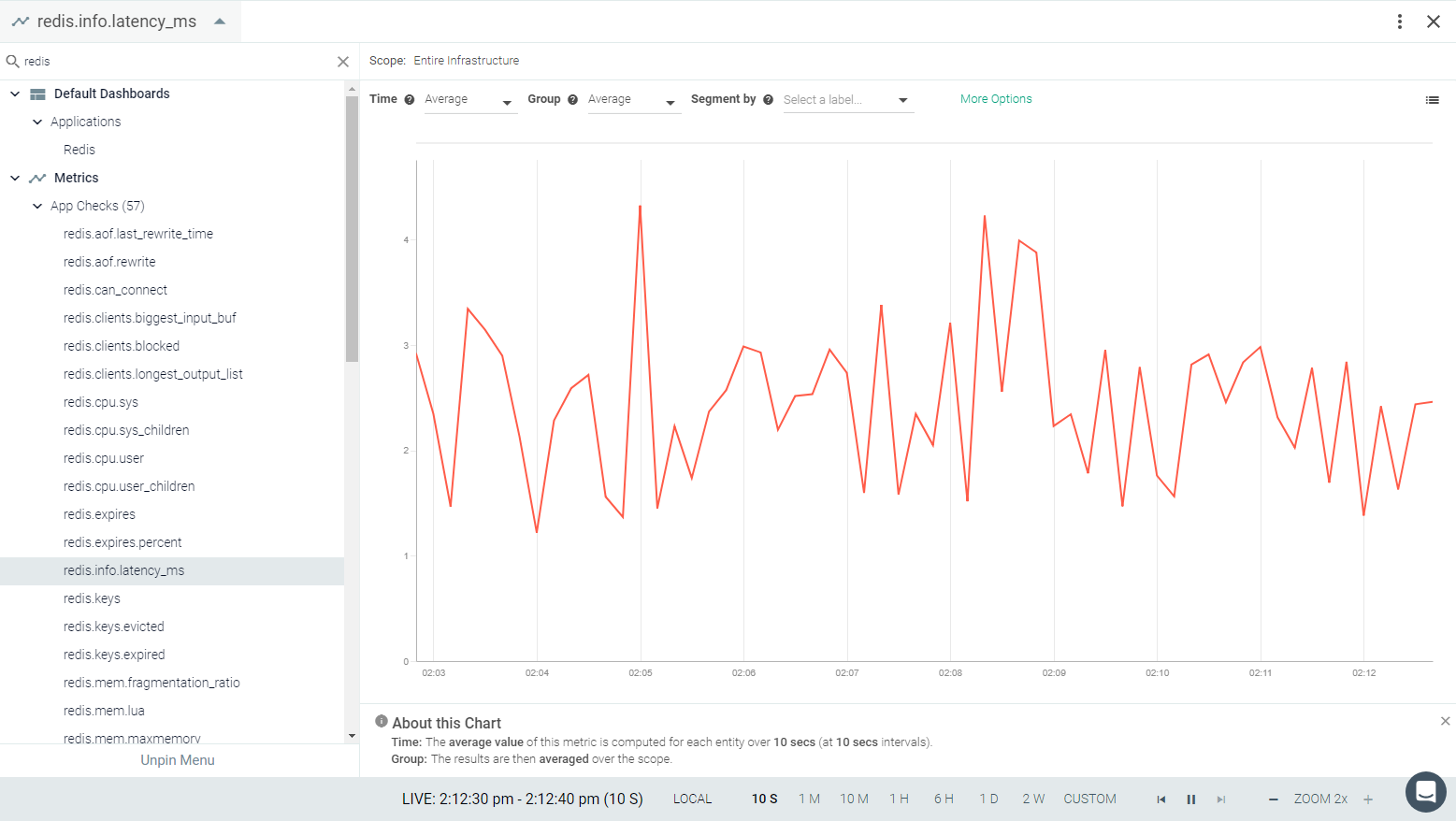
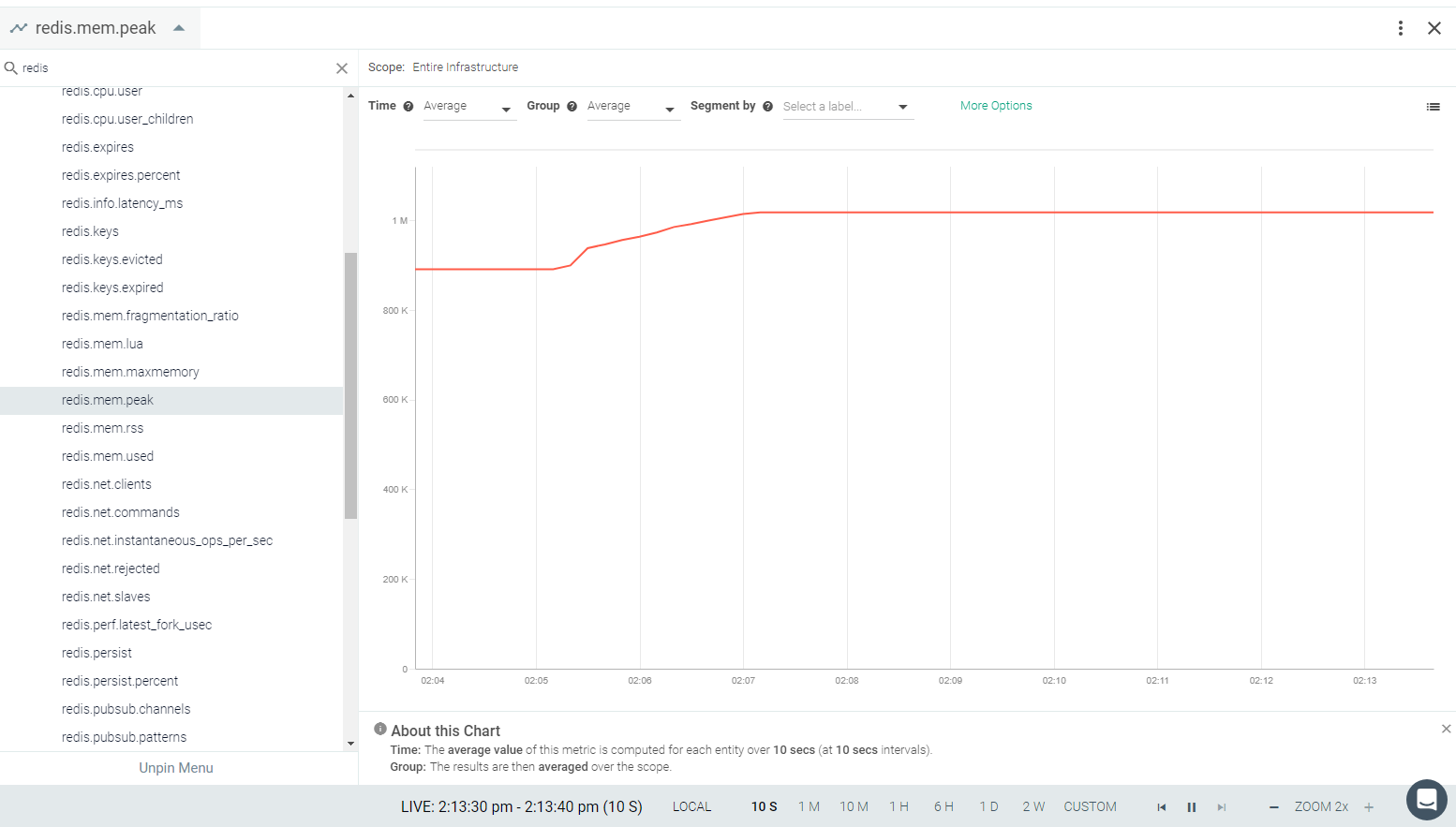
Result in the Monitor UI