NTP
If the NTP check is enabled in the Sysdig agent, it reports the time offset of the local agent from an NTP server.
This page describes how to edit the configuration to collect information, the metrics available for integration, and a sample result in the Sysdig Monitor UI.
Sysdig Agent Configuration
Review how to Edit dragent.yaml to Integrate or Modify Application Checks.
Default Configuration
By default, Sysdig's dragent.default.yaml does not provide any
configuration for NTP.
Add the configuration in Example 1 to the dragent.yaml file to enable
NTP checks.
Never edit dragent.default.yaml directly; always edit only
dragent.yaml.
Example
- name: ntp
interval: 60
pattern:
comm: systemd
conf:
host: us.pool.ntp.org
offset_threshold: 60
host: (mandatory) provides the host name ofNTPserver.offset_threshold: (optional) provides the difference (in seconds) between the local clock and the NTP server, when thentp.in_syncservice check becomesCRITICAL. The default is60seconds.
Metrics Available
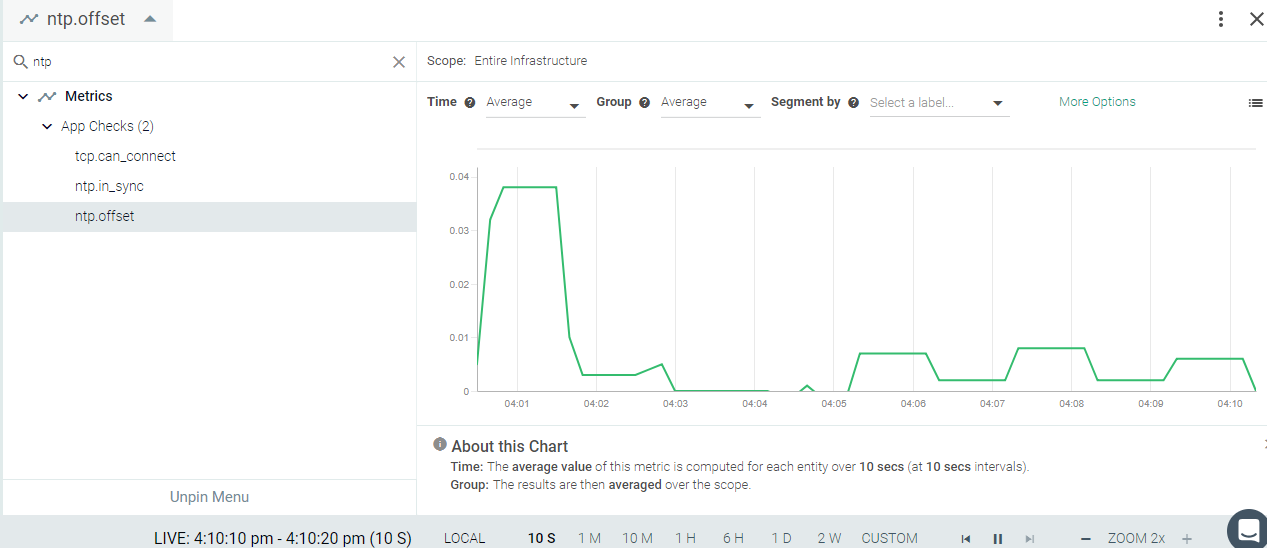
ntp.offset, the time difference between the local clock and the NTP
reference clock, is the primary NTP metric.
See also NTP Metrics.
Service Checks
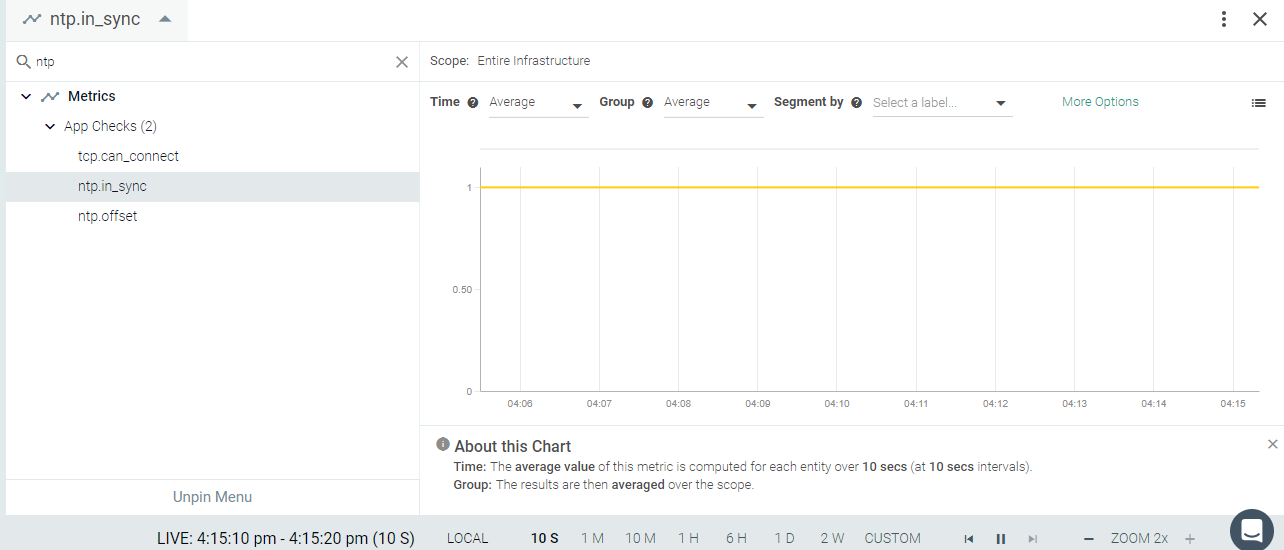
ntp.in_sync:
Returns CRITICAL if the NTP offset is greater than the threshold
specified in dragent.yaml, otherwise OK.
Result in the Monitor UI